Cell:鉴定出非小细胞肺癌癌基因GLDC
2012-01-22 MedSci MedSci原创
新加坡研究人员证实一种代谢酶甘氨酸脱羧化酶(glycine decarboxylase, GLDC)对非小细胞肺癌(non-small-cell lung cancer)中肿瘤始发细胞(tumor-initiating cell, TIC)是比较关键的。来自原发性非小细胞肺癌的肿瘤始发细胞表达高水平的癌干细胞因子LIN28B和甘氨酸脱羧化酶,这两者对于肿瘤始发细胞的生长和肿瘤发生是必需的。过表达甘
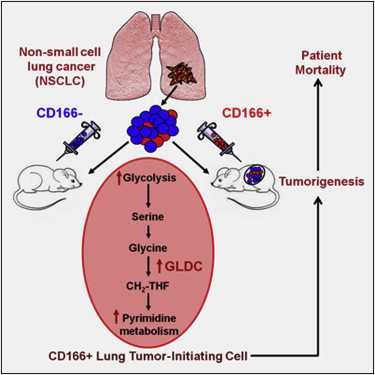
新加坡研究人员证实一种代谢酶甘氨酸脱羧化酶(glycine decarboxylase, GLDC)对非小细胞肺癌(non-small-cell lung cancer)中肿瘤始发细胞(tumor-initiating cell, TIC)是比较关键的。来自原发性非小细胞肺癌的肿瘤始发细胞表达高水平的癌干细胞因子LIN28B和甘氨酸脱羧化酶,这两者对于肿瘤始发细胞的生长和肿瘤发生是必需的。过表达甘氨酸脱羧化酶和其他甘氨酸/丝氨酸酶,而不是催化上没有活性的甘氨酸脱羧化酶,促进细胞转化和肿瘤发生。这就表明甘氨酸脱羧化酶是一种促进正常细胞转化为癌细胞的癌基因。
研究人员还发现甘氨酸脱羧化酶促进糖酵解和甘氨酸/丝氨酸代谢发生显著的变化,从而导致嘧啶碱基代谢发生变化以便调节癌细胞增殖。在诊所中,甘氨酸脱羧化酶的异常激活与肺癌病人更差的存活能力相关联在一起,这样人们可以利用甘氨酸脱羧化酶的表达情况来预测非小细胞肺癌的死亡率。另外,研究人员也在多种癌症类型中观察到异常的甘氨酸脱羧化酶表达。甘氨酸代谢和肿瘤发生之间的联系可能为开发抗癌治疗提供新的靶标。(生物谷:towersimper编译)
Glycine Decarboxylase Activity Drives Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumor-Initiating Cells and Tumorigenesis
Wen Cai Zhang, Ng Shyh-Chang, He Yang, Amit Rai, Shivshankar Umashankar, Siming Ma, Boon Seng Soh, Li Li Sun, Bee Choo Tai, Min En Nga, Kishore Kumar Bhakoo, Senthil Raja Jayapal, Massimo Nichane, Qiang Yu, Dokeu A. Ahmed, Christie Tan, Wong Poo Sing, John Tam, Agasthian Thirugananam, Monireh Soroush Noghabi, Yin Huei Pang, Haw Siang Ang, Paul Robson, Philipp Kaldis, Ross Andrew Soo, Sanjay Swarup, Elaine Hsuen Lim, Bing Lim
Identification of the factors critical to the tumor-initiating cell (TIC) state may open new avenues in cancer therapy. Here we show that the metabolic enzyme glycine decarboxylase (GLDC) is critical for TICs in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). TICs from primary NSCLC tumors express high levels of the oncogenic stem cell factor LIN28B and GLDC, which are both required for TIC growth and tumorigenesis. Overexpression of GLDC and other glycine/serine enzymes, but not catalytically inactive GLDC, promotes cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. We found that GLDC induces dramatic changes in glycolysis and glycine/serine metabolism, leading to changes in pyrimidine metabolism to regulate cancer cell proliferation. In the clinic, aberrant activation of GLDC correlates with poorer survival in lung cancer patients, and aberrant GLDC expression is observed in multiple cancer types. This link between glycine metabolism and tumorigenesis may provide novel targets for advancing anticancer therapy.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言









#CEL#
53
#非小细胞#
64
#Cell#
54
#癌基因#
69