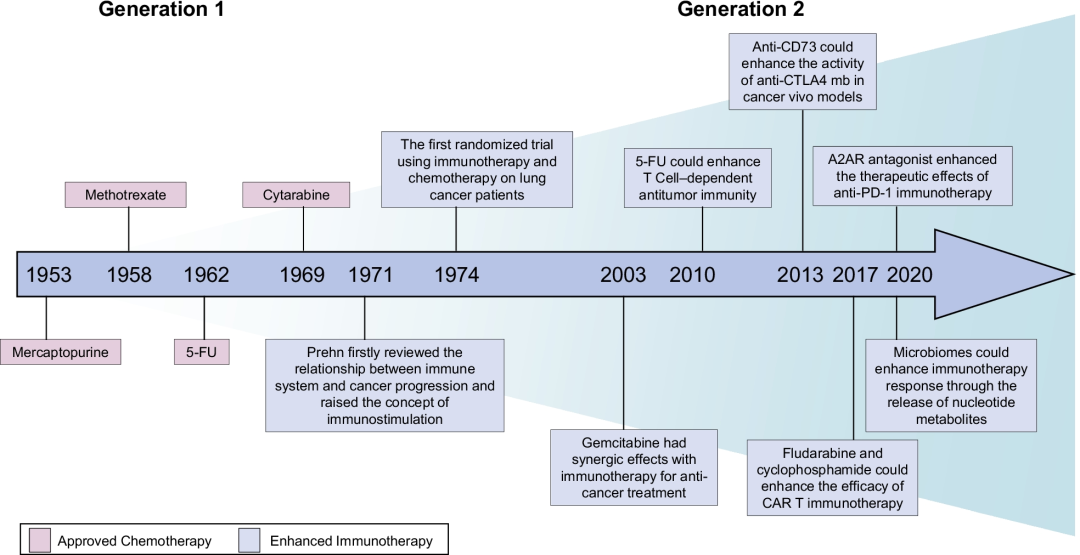
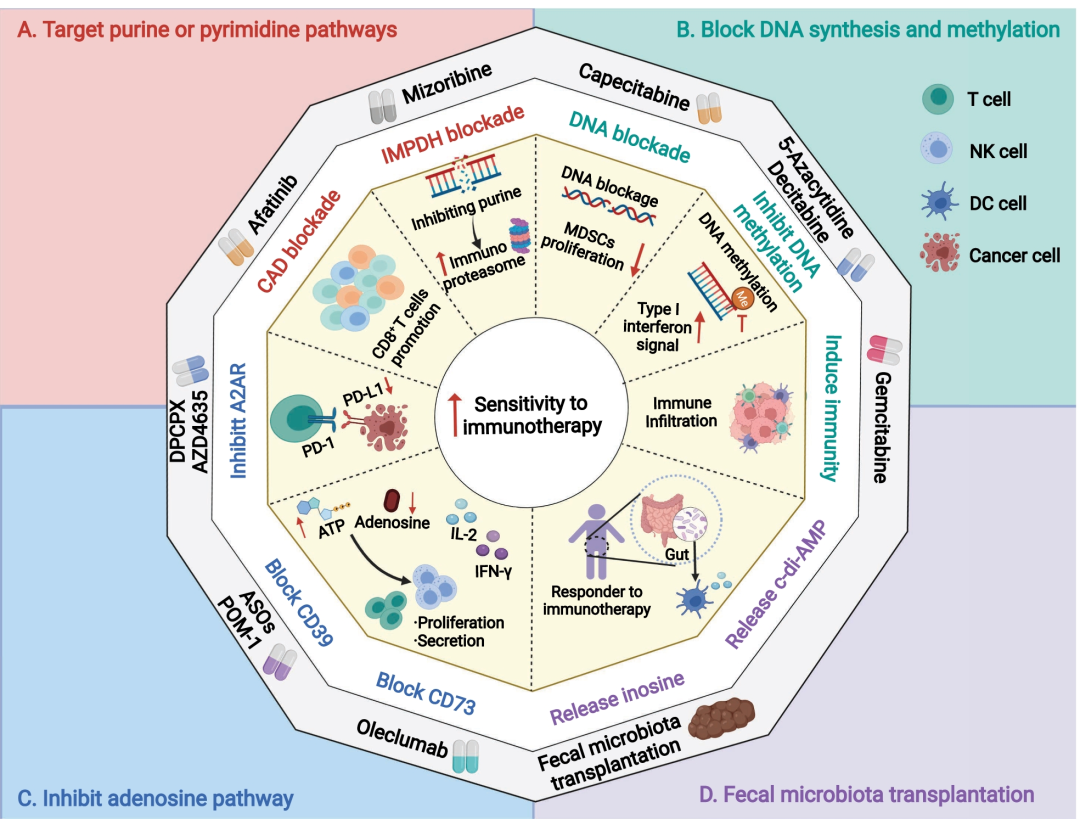
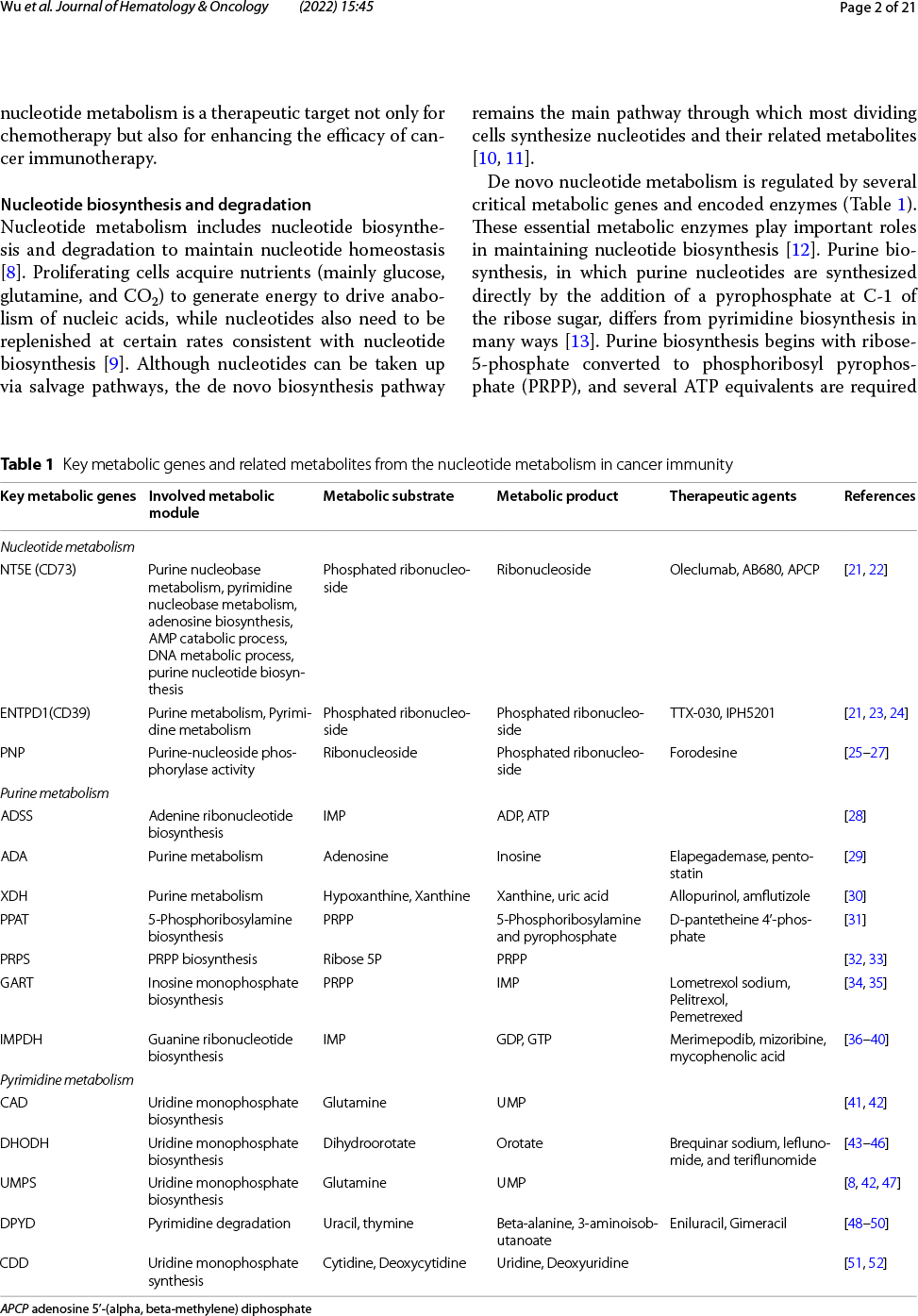
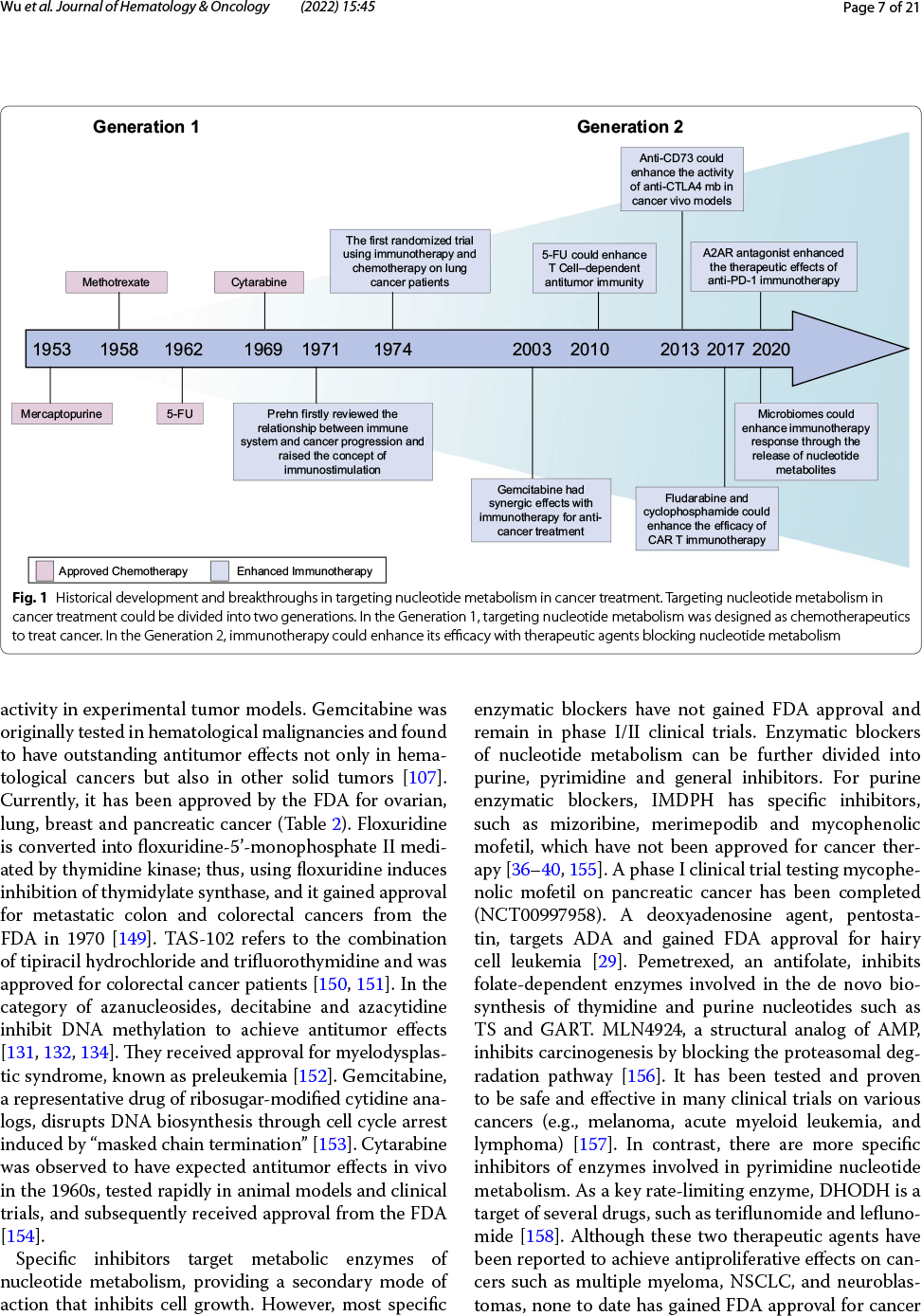
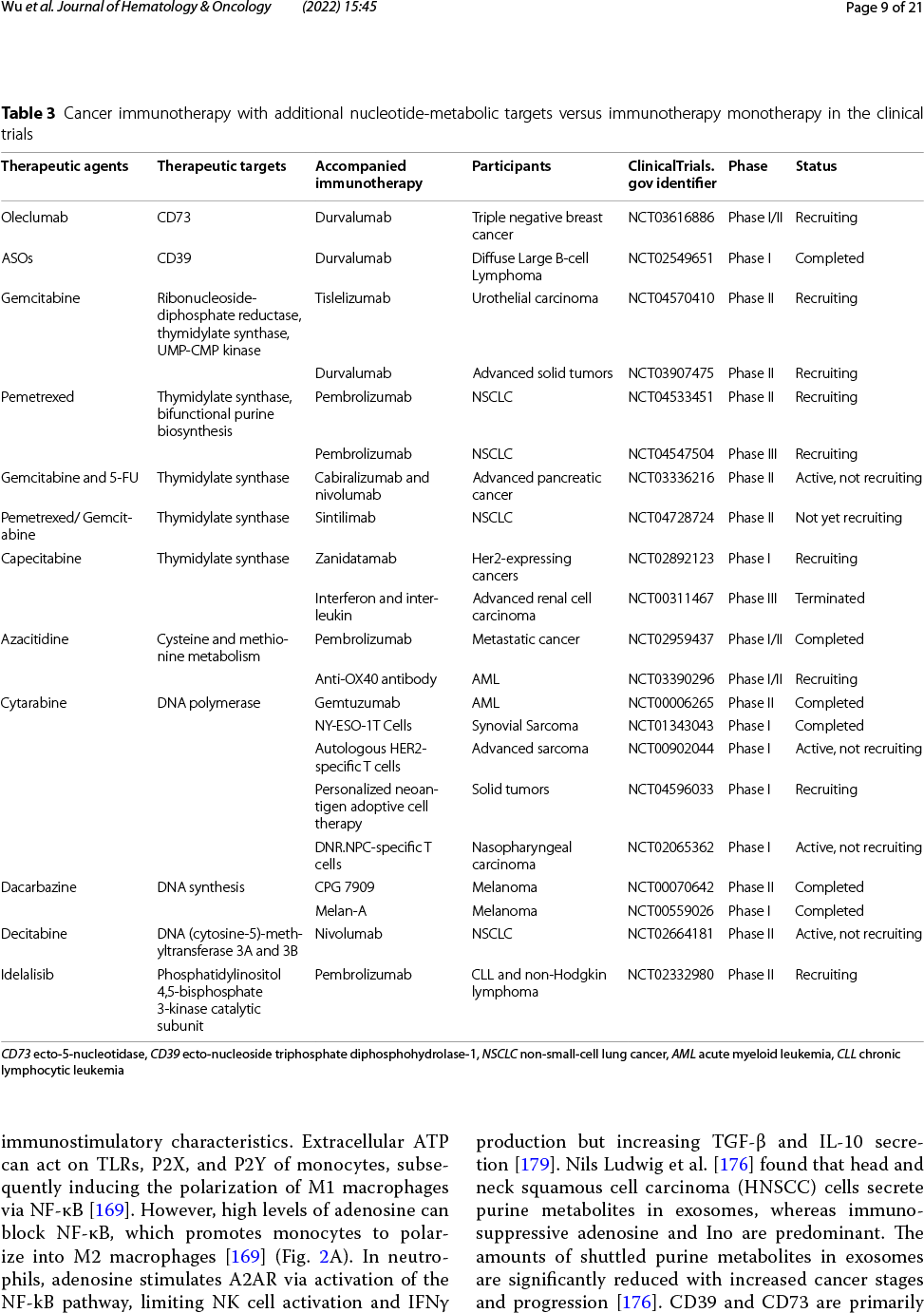
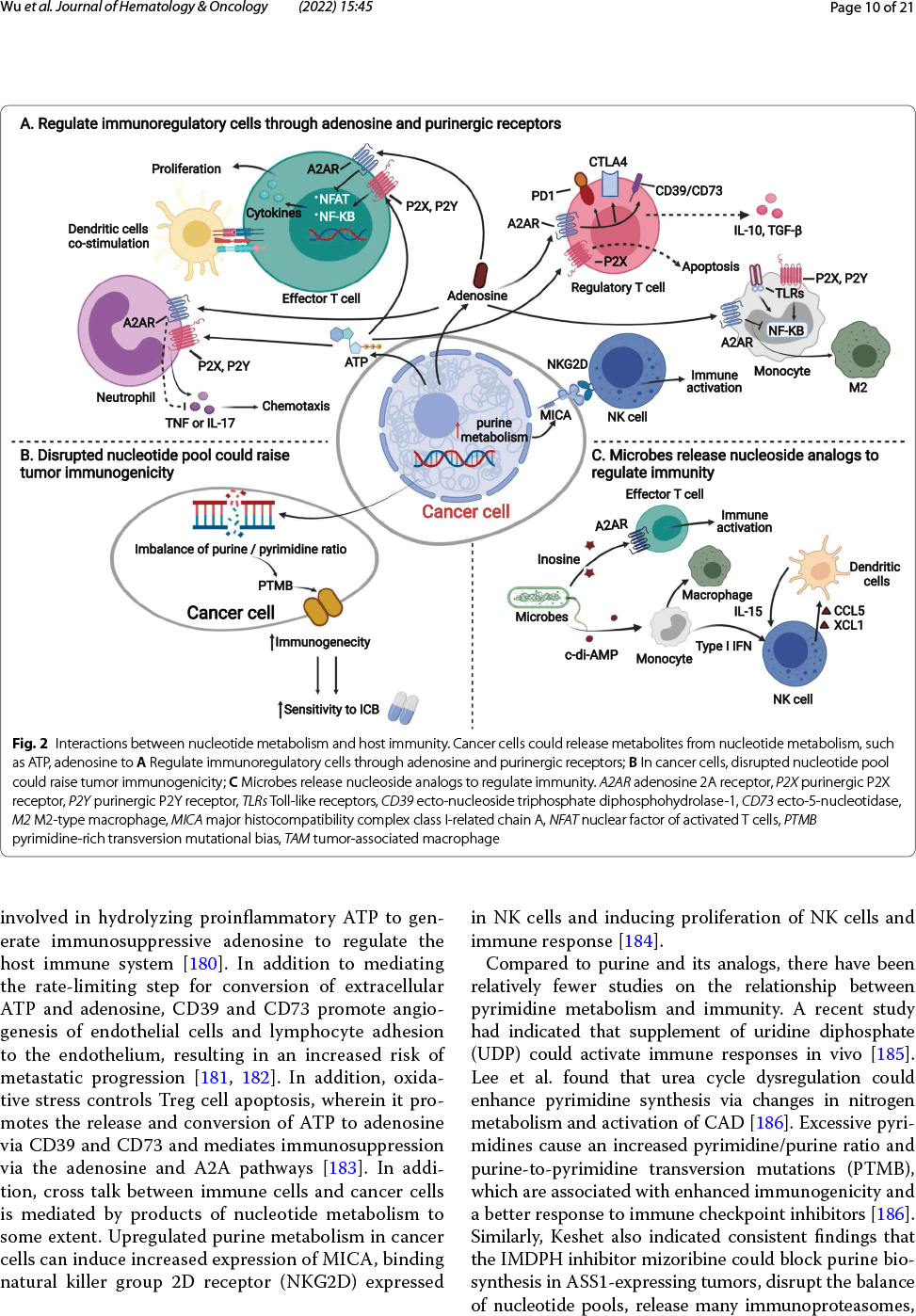
核酸由核苷酸组成,主要负责携带和传递正常细胞或肿瘤细胞的遗传信息。虽然抗核苷酸代谢可抑制肿瘤的发生和发展,但是也可能对正常细胞产生严重的副作用。随着对核苷酸代谢的深入研究,科学家们发现肿瘤核苷酸代谢失调对于肿瘤免疫逃逸具有促进作用,表明抑制核苷酸代谢产物可能增强免疫治疗效果。近年来越来越多的证据支持抗核苷酸代谢可通过以下方式增强抗肿瘤免疫反应:①通过维持腺苷和三磷酸腺苷等若干重要代谢产物浓度,从而激活宿主免疫系统;②通过破坏嘌呤和嘧啶库、提高基因突变性和基因组不稳定性,从而促进免疫原性;③通过微生物释放核苷类似物,从而调节免疫。核苷酸代谢靶向治疗方法结合免疫治疗,已经对临床前动物模型取得了令人鼓舞的成功。
2022年4月27日,英国生物医学中心旗下《血液学与肿瘤学杂志》在线发表复旦大学附属肿瘤医院吴怀亮、龚悦、吉芃、谢亦璠、江一舟、柳光宇等学者的长篇综述,系统回顾了核苷酸代谢失调如何促进肿瘤生长并与宿主免疫系统相互作用,并为靶向核苷酸代谢用于各种恶性肿瘤的免疫治疗提供了新方向。全文长达21页,参考文献多达254篇。

J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Apr 27;15(1):45.
Targeting nucleotide metabolism: a promising approach to enhance cancer immunotherapy.
Wu HL, Gong Y, Ji P, Xie YF, Jiang YZ, Liu GY.
Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China.
Targeting nucleotide metabolism can not only inhibit tumor initiation and progression but also exert serious side effects. With in-depth studies of nucleotide metabolism, our understanding of nucleotide metabolism in tumors has revealed their non-proliferative effects on immune escape, indicating the potential effectiveness of nucleotide antimetabolites for enhancing immunotherapy. A growing body of evidence now supports the concept that targeting nucleotide metabolism can increase the antitumor immune response by (1) activating host immune systems via maintaining the concentrations of several important metabolites, such as adenosine and ATP, (2) promoting immunogenicity caused by increased mutability and genomic instability by disrupting the purine and pyrimidine pool, and (3) releasing nucleoside analogs via microbes to regulate immunity. Therapeutic approaches targeting nucleotide metabolism combined with immunotherapy have achieved exciting success in preclinical animal models. Here, we review how dysregulated nucleotide metabolism can promote tumor growth and interact with the host immune system, and we provide future insights into targeting nucleotide metabolism for immunotherapeutic treatment of various malignancies.
PMID: 35477416
DOI: 10.1186/s13045-022-01263-x
















本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言












#核苷酸#
87