PLoS ONE:埃可病毒诱导神经元细胞死亡的机制
2012-05-10 Deepblue 生物谷
埃可30型肠道病毒(Echo30)能够引起无菌性脑膜炎,是目前研究得较热的人类肠道病毒(EVs)之一。目前,由Echo30感染所引起的显著临床结果的潜在机制还不明确。 近日,来自韩国国家卫生研究院的研究人员Doo-Sung Cheon发现,通过激活TRIO-RhoA信号,Echo30诱导了神经元细胞的死亡。相关论文发表在5月7日的PLoS ONE。 该研究的目的在于阐明Echo30感染所引起的

埃可30型肠道病毒(Echo30)能够引起无菌性脑膜炎,是目前研究得较热的人类肠道病毒(EVs)之一。目前,由Echo30感染所引起的显著临床结果的潜在机制还不明确。
近日,来自韩国国家卫生研究院的研究人员Doo-Sung Cheon发现,通过激活TRIO-RhoA信号,Echo30诱导了神经元细胞的死亡。相关论文发表在5月7日的PLoS ONE。
该研究的目的在于阐明Echo30感染所引起的神经元细胞分子病理的改变。基于二维凝胶电泳(2-DE)及MALDI-TOF/TOF质谱分析等蛋白质组学的分析方法,他们研究了神经元细胞对Echo30感染的应答反应。
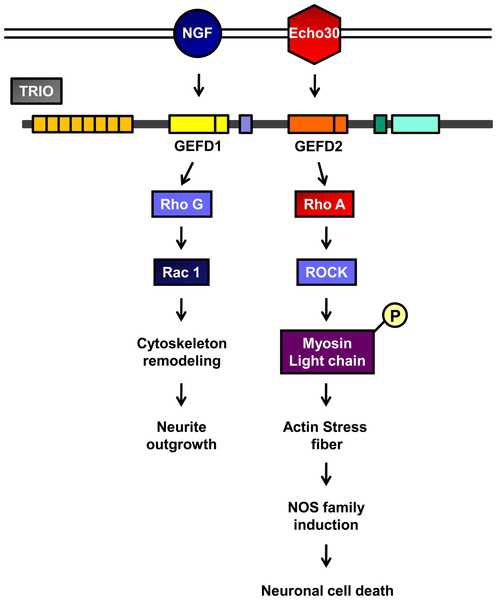
在Echo30感染的SK-N-SH细胞,他们发现几种特定蛋白的表达水平有着显著改变。特别是SK-N-SH细胞的三级功能区(TRIO),在感染后发生了显著上调。
一般来说,TRIO是调节轴突导向及细胞迁移的一个关键组分。在这项研究里,他们惊奇的发现,TRIO在Echo30诱导的神经元细胞死亡过程中具有重要作用。Echo30的感染激活了TRIO-鸟苷酸交换因子结构域(GEFD2),反过来激活了RhoA信号。
这些结果表明,Echo30的感染通过激活TRIO-RhoA信号诱导了神经元细胞的死亡。对此,Doo-Sung Cheon表示,在治疗由Echo30诱导的无菌性脑膜炎过程中,对TRIO-RhoA信号的调节可能会是一个新的治疗途经。

doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036656
PMC:
PMID:
Echovirus 30 Induced Neuronal Cell Death through TRIO-RhoA Signaling Activation
June-Woo Lee, Sang-Gu Yeo, Byung-Hak Kang, Hoe-Kyu Lee, Jin-Won Kim, Sun-Hwa Lee, Ki-Sang Kim, Doo-Sung Cheon.
Echovirus 30 (Echo30) is one of the most frequently identified human enteroviruses (EVs) causing aseptic meningitis and encephalitis. However the mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of Echo30 infection with significant clinical outcomes is not completely understood.The aim of this investigation is to illustrate molecular pathologic alteration in neuronal cells induced by Echo30 infection using clinical isolate from young patient with neurologic involvement.To characterize the neuronal cellular response to Echo30 infection, we performed a proteomic analysis based on two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) and MALDI-TOF/TOF Mass Spectrophotometric (MS) analysis.We identified significant alteration of several protein expression levels in Echo30-infected SK-N-SH cells. Among these proteins, we focused on an outstanding up-regulation of Triple functional domain (TRIO) in Echo30-infected SK-N-SH cells.Generally, TRIO acts as a key component in the regulation of axon guidance and cell migration. In this study, we determined that TRIO plays a role in the novel pathways in Echo30 induced neuronal cell death.Our finding shows that TRIO plays a critical role in neuronal cell death by Echo30 infection. Echo30 infection activates TRIO-guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) domains (GEFD2) and RhoA signaling in turn.
These results suggest that Echo30 infection induced neuronal cell death by activation of the TRIO-RhoA signaling.We expect the regulation of TRIO-RhoA signaling may represent a new therapeutic approach in treating aseptic meningitis and encephalitis induced by Echo30.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言











#Plos one#
93