Current Biology:黑暗疗法有助视力恢复
2013-03-06 生物无忧 生物无忧
在一项新的研究中,研究人员通过研究患有一种被称作弱视(amblyopia)的视力障碍(visual impairment)的小猫在完全黑暗的环境中呆上10天之前和之后的结果,发现恢复视力有时可能比较简单,关灯即可.相关研究结果于2013年2月14日发表在Current Biology期刊上,论文标题为"Darkness alters maturation of visual cortex and
在一项新的研究中,研究人员通过研究患有一种被称作弱视(amblyopia)的视力障碍(visual impairment)的小猫在完全黑暗的环境中呆上10天之前和之后的结果,发现恢复视力有时可能比较简单,关灯即可.相关研究结果于2013年2月14日发表在Current Biology期刊上,论文标题为"Darkness alters maturation of visual cortex and promotes fast recovery from monocular deprivation".
加拿大达尔豪斯大学研究员Kevin Duffy和Donald Mitchell认为暴露在黑暗中导致视觉系统中的一些部分恢复到发育的早期阶段,从而具有更大的灵活性.
Duffy说,"可能存在不需药物介入就可增加大脑可塑性和从诸如弱视之类的疾病中恢复过来的方法.沉浸在完全黑暗的环境中似乎重置视觉脑区而使得能够发生强劲恢复."
当在生命早期两只眼睛不能同样看得非常清楚时,弱视就被认为产生了,因而眼睛到大脑中视觉区域之间的连接仍然需要加以改善.如果没有治疗的话,那么视力不平衡能够导致永久性的视力丧失.
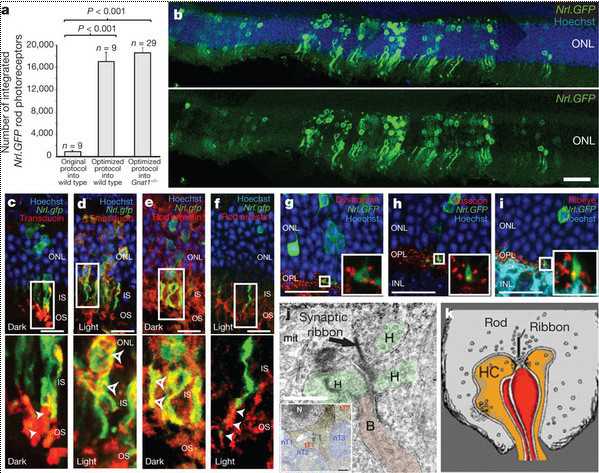
在这项新的研究中,研究人员研究了通过实验性阻止视觉输入到一只眼睛而患上弱视的小猫.当这些动物被放置在黑暗环境之后,它们的视力发生深刻的和快速的恢复.进一步的研究提示着视力恢复依赖于让视觉系统保持在原位的神经丝丧失.随着这些稳定性的成分消失,视觉系统能够自由地进行自我矫正.
研究人员说,黑暗疗法(darkness therapy)有望治疗弱视儿童,但是不要在家中尝试这种疗法.他们认为必须是完全黑暗且在任何时刻没有任何杂光的情形下才能发挥作用.首先找出弱视产生的初始原因也是同样重要的,这样才能确保在黑暗中呆上一段时间将不会对个人视力较好的那只眼睛带来伤害.
研究人员仍然正在确定出需要多大程度的黑暗和需要在黑暗环境中呆上多长的时间.他们说,无论如何,药物不可能足够地达到他们观察到的黑暗疗法的疗效。
与视力相关的拓展阅读:
- PLoS One:联合生长因子抑制剂可减少糖尿病小鼠的视力损害
- Sci Reports:常人也可获“超级视力”
- Nature:注射感光细胞有助视力恢复
- IOVS:标准视力测试能预知夜间驾驶能力吗?
- NEJM:一例有视力模糊和肾功能衰竭的22岁女患者[病例讨论] 更多信息请点击:有关视力更多资讯

DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2013.01.017
PMC:
PMID:
Darkness Alters Maturation of Visual Cortex and Promotes Fast Recovery from Monocular Deprivation
Kevin R. Duffy, Donald E. Mitchell
Highlights
Neurofilament is reduced in kitten visual cortex after a short period of darkness ? Darkness immediately after monocular deprivation prevents development of amblyopia ? Darkness imposed after amblyopia develops results in its disappearance in 5 to 7 days ? Short (10 day) periods of darkness may boost recovery from amblyopia in humans
Summary
The existence of heightened brain plasticity during critical periods in early postnatal life is a central tenet of developmental sensory neuroscience and helps explain the enduring deficits induced by early abnormal sensory exposure [1,2]. The human visual disorder amblyopia has been linked to unbalanced visual input to the two eyes in early postnatal visual cortical development and has been modeled in animals by depriving them of patterned visual input to one eye [3,4], a procedure known as monocular deprivation (MD). We investigated the possibility that a period of darkness might reset the central visual pathways to a more plastic stage and hence increase the capacity for recovery from early MD. Here we show that a 10 day period of complete darkness reverses maturation of stable cytoskeleton components in kitten visual cortex and also results in rapid elimination of, or even immunity from, visual deficits linked to amblyogenic rearing by MD. The heightened instability of the cytoskeleton induced by darkness likely represents just one of many parallel molecular changes that promote visual recovery, possibly by release of the various brakes on cortical plasticityduced
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言








#Bio#
66
#Biol#
69