JCI:乳腺癌中SIX1诱导淋巴管形成及转移的机制
2012-04-10 Deepblue 生物谷
乳腺癌中淋巴结转移及不良预后的关系10年以前就已经被发现。然而,癌细胞侵入淋巴系统的机理还没有被完全阐明。 最近的研究发现,在转移性传播中,由于肿瘤分泌的生长因子刺激了淋巴管的形成,淋巴系统起到了一个积极的作用。 SIX1是一种与乳腺癌有关的同源结构域转录因子,它是否与淋巴管形成及淋巴转移有关还未可知,对此,美国科罗拉多大学丹佛医学院的研究人员开展了一项研究。 在一个注入了人类乳腺癌细胞的免

乳腺癌中淋巴结转移及不良预后的关系10年以前就已经被发现。然而,癌细胞侵入淋巴系统的机理还没有被完全阐明。
最近的研究发现,在转移性传播中,由于肿瘤分泌的生长因子刺激了淋巴管的形成,淋巴系统起到了一个积极的作用。
SIX1是一种与乳腺癌有关的同源结构域转录因子,它是否与淋巴管形成及淋巴转移有关还未可知,对此,美国科罗拉多大学丹佛医学院的研究人员开展了一项研究。
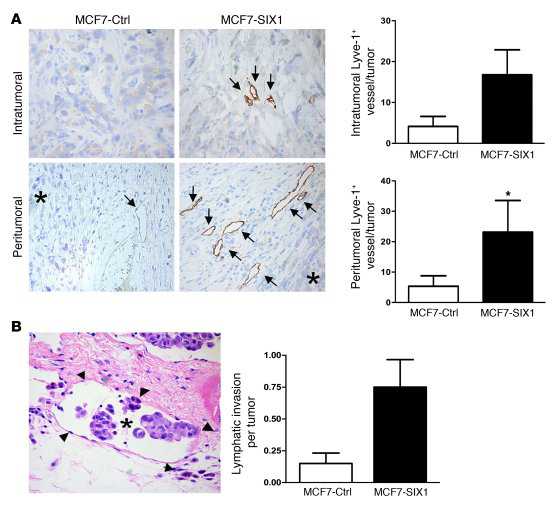
在一个注入了人类乳腺癌细胞的免疫缺陷小鼠模型中,他们发现SIX1的表达促进了癌周及癌内的淋巴管形成、淋巴入侵以及乳腺癌细胞的远端转移。
SIX1能够引起促淋巴生成因子VEGF-C的转录,这对淋巴管生成及淋巴转移也是必需的。通过使用一个老鼠乳腺癌模型,结果发现VEGF-C不足以介导SIX1所有的转移效应,这表明SIX1通过了额外的不依赖VEGF-C的通路来行使作用。
最后,他们通过阐明SIX1及VEGF-C在人类乳腺癌的联合表达,验证了SIX1/VEGF-C的临床意义。
这些数据明确了SIX1在乳腺癌淋巴扩散中关键性的作用,阐明了乳腺癌中VEGF-C的表达是如何上调并导致淋巴管生成及转移。相关论文发表在4月2日的The Journal of Clinical Investigation(生物谷Deepblue编译)

doi: 10.1172/JCI59858
PMC:
PMID:
SIX1 induces lymphangiogenesis and metastasis via upregulation of VEGF-C in mouse models of breast cancer
Chu-An Wang, Paul Jedlicka, Aaron N. Patrick, Douglas S. Micalizzi, Kimberly C. Lemmer, Erin Deitsch, Matias Casás-Selves, J. Chuck Harrell and Heide L. Ford.
An association between lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in breast cancer was observed decades ago. However, the mechanisms by which tumor cells infiltrate the lymphatic system are not completely understood.Recently, it has been proposed that the lymphatic system has an active role in metastatic dissemination and that tumor-secreted growth factors stimulate lymphangiogenesis.We therefore investigated whether SIX1, a homeodomain-containing transcription factor previously associated in breast cancer with lymph node positivity, was involved in lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis.In a model in which human breast cancer cells were injected into immune-compromised mice, we found that SIX1 expression promoted peritumoral and intratumoral lymphangiogenesis, lymphatic invasion, and distant metastasis of breast cancer cells.SIX1 induced transcription of the prolymphangiogenic factor VEGF-C, and this was required for lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Using a mouse mammary carcinoma model, we found that VEGF-C was not sufficient to mediate all the metastatic effects of SIX1, indicating that SIX1 acts through additional,VEGF-C–independent pathways.Finally, we verified the clinical significance of this prometastatic SIX1/VEGF-C axis by demonstrating coexpression of SIX1 and VEGF-C in human breast cancer.These data define a critical role for SIX1 in lymphatic dissemination of breast cancer cells, providing a direct mechanistic explanation for how VEGF-C expression is upregulated in breast cancer, resulting in lymphangiogenesis and metastasis
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言












#JCI#
48
#淋巴管#
0