Nucleic Acids Res:郭安源等在急性T淋巴细胞白血病发病机理研究中取得新进展
2012-04-10 华中科技大学生命科学与技术学院 华中科技大学生命科学与技术学院
2月23日,著名研究期刊《Nucleic Acids Research》在线发表了华中科技大学生命科学与技术学院郭安源研究小组的研究论文,报告了关于急性T淋巴细胞白血病中miRNA和转录因子共调控网络的生物信息学研究的最新成果。 急性T淋巴细胞白血病(T-ALL)是一种恶性血液疾病,其治疗效果和预后比更常见的B细胞系淋巴细胞白血病通常要差很多,具体分子机理和调控机

2月23日,著名研究期刊《Nucleic Acids Research》在线发表了华中科技大学生命科学与技术学院郭安源研究小组的研究论文,报告了关于急性T淋巴细胞白血病中miRNA和转录因子共调控网络的生物信息学研究的最新成果。
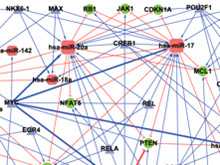
急性T淋巴细胞白血病(T-ALL)是一种恶性血液疾病,其治疗效果和预后比更常见的B细胞系淋巴细胞白血病通常要差很多,具体分子机理和调控机理还不清楚。郭安源教授课题组以miRNA和转录因子的共调控角度为切入点,运用生物信息学方法,预测miRNA和转录因子与疾病基因之间形成的共调控前馈环模块,并由此构建共调控网络。通过深入分析该调控网络获得了其中的核心miRNA和基因。并进一步对其中核心基因miR-19与CYLD在T-ALL中的分子机理进行了研究,首次揭示了miR-19抑制CYLD蛋白的产生,继而激活下游的NFKB信号通路,导致T淋巴细胞增殖失控。
这项研究成果从系统网络水平研究急性T淋巴细胞白血病的发病机理和调控过程,为其诊断和治疗提供理论依据,并为复杂疾病的研究提供了计算和实验交叉的新思路和方法。(生物谷 bioon.com)

doi:10.1093/nar/gks175
PMC:
PMID:
MicroRNA and transcription factor co-regulatory network analysis reveals miR-19 inhibits CYLD in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Huashan Ye,Xiaowen Liu, Meng Lv, Yuliang Wu, Shuzhen Kuang, Jing Gong, Ping Yuan, Zhaodong Zhong, Qiubai Li, Haibo Jia, Jun Sun, Zhichao Chen,An-Yuan Guo
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive hematological malignancy. The understanding of its gene expression regulation and molecular mechanisms still remains elusive. Started from experimentally verified T-ALL-related miRNAs and genes, we obtained 120 feed-forward loops (FFLs) among T-ALL-related genes, miRNAs and TFs through combining target prediction. Afterwards, a T-ALL miRNA and TF co-regulatory network was constructed, and its significance was tested by statistical methods. Four miRNAs in the miR-17–92 cluster and four important genes (CYLD, HOXA9, BCL2L11 and RUNX1) were found as hubs in the network. Particularly, we found that miR-19 was highly expressed in T-ALL patients and cell lines. Ectopic expression of miR-19 represses CYLD expression, while miR-19 inhibitor treatment induces CYLD protein expression and decreases NF-κB expression in the downstream signaling pathway. Thus, miR-19, CYLD and NF-κB form a regulatory FFL, which provides new clues for sustained activation of NF-κB in T-ALL. Taken together, we provided the first miRNA-TF co-regulatory network in T-ALL and proposed a model to demonstrate the roles of miR-19 and CYLD in the T-cell leukemogenesis. This study may provide potential therapeutic targets for T-ALL and shed light on combining bioinformatics with experiments in the research of complex diseases.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言












#发病机理#
73
#T淋巴细胞白血病#
83
#acid#
65
#淋巴细胞白血病#
60
#CID#
60
#淋巴细胞#
48
#T淋巴细胞#
51