Blood:发现控制髓系分化的关键调节因子
2012-07-03 Deepblue 生物谷
近日,来自中国医学科学院研究员张俊武所在的课题组研究发现,miR-29a及miR-142-3p是髓系分化及急性髓细胞性白血病的关键调节因子。相关研究成果于5月24日发表在Blood上。 目前,microRNAs被发现与包括造血作用在内的不同生理学过程息息相关,但是,它们对髓系发育的作用还不明确。研究人员发现,白血病细胞系以及CD34+造血干/祖细胞在髓系分化期间,miR-29a及miR-142-

近日,来自中国医学科学院研究员张俊武所在的课题组研究发现,miR-29a及miR-142-3p是髓系分化及急性髓细胞性白血病的关键调节因子。相关研究成果于5月24日发表在Blood上。
目前,microRNAs被发现与包括造血作用在内的不同生理学过程息息相关,但是,它们对髓系发育的作用还不明确。研究人员发现,白血病细胞系以及CD34+造血干/祖细胞在髓系分化期间,miR-29a及miR-142-3p表现上调。
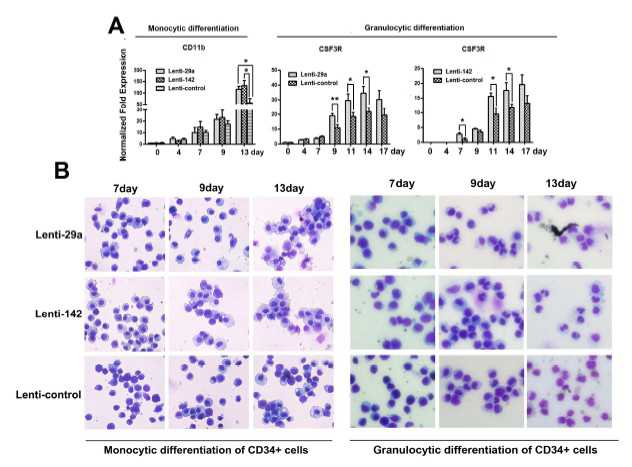
研究发现,这两种miRNAs促进了佛波酯诱导的单核细胞及全反式视黄酸诱导的粒细胞的分化。而且,这两种miRNAs直接抑制了细胞周期蛋白T2基因,阻止了低磷酸化的Rb蛋白的释放,诱导了单核细胞的分化。
除此以外,他们还发现,miR-29a的靶点细胞周期素依赖性激酶6基因,以及miR-142-3p的靶点TGF-β激活的激酶1/MAP3K结合蛋白2基因,都与单核及粒细胞分化的调节有关。
在急性髓细胞性白血病,miR-29a及miR-142-3p水平表现出显著下降,而它们的靶蛋白水平则表现出明显的上升。
通过慢病毒介导的基因转染,在来自健康对照组以及急性髓细胞性白血病患者的造血干/祖细胞内表达miR-29a或miR-142-3p,都能够下调它们靶点的表达,并促进髓系分化。
总的来说,该研究表明,miR-29a及miR-142-3p是正常髓系分化的关键调节因子,而且,它们表达的降低还与急性髓细胞性白血病的发展有关。

doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-385716
PMC:
PMID:
MicroRNA-29a and microRNA-142-3p are regulators of myeloid differentiation and acute myeloid leukemia
Xiao-Shuang Wang, Jia-Nan Gong, Jia Yu, Fang Wang, Xin-Hua Zhang, Xiao-Lin Yin, Zhen-Qing Tan, Zi-Mian Luo, Gui-Hua Yang, Chao Shen, and Jun-Wu Zhang.
Although microRNAs (miRNAs) are increasingly linked to various physiologic processes, including hematopoiesis, their function in the myeloid development is poorly understood. We detected up-regulation of miR-29a and miR-142-3p during myeloid differentiation in leukemia cell lines and CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells.By gain-of-function and loss-of-function experiments, we demonstrated that both miRNAs promote the phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate–induced monocytic and all-trans-retinoic acid-induced granulocytic differentiation of HL-60, THP-1, or NB4 cells. Both the miRNAs directly inhibited cyclin T2 gene, preventing the release of hypophosphorylated retinoblastoma and resulting in induction of monocytic differentiation.In addition, a target of miR-29a, cyclin-dependent kinase 6 gene, and a target of miR-142-3p, TGF-β–activated kinase 1/MAP3K7 binding protein 2 gene, are involved in the regulation of both monocytic and granulocytic differentiation. A significant decrease of miR-29a and 142-3p levels and an obvious increase in their target protein levels were also observed in blasts from acute myeloid leukemia.By lentivirus-mediated gene transfer, we demonstrated that enforced expression of either miR-29a or miR-142-3p in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells from healthy controls and acute myeloid leukemia patients down-regulated expression of their targets and promoted myeloid differentiation. These findings confirm that miR-29a and miR-142-3p are key regulators of normal myeloid differentiation and their reduced expression is involved in acute myeloid leukemia development.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言









#调节因子#
66