Science:“证”- 疾病诊疗的系统生物学方法
2014-12-25 徐安龙 树兰医疗
【树兰点评】 当西医进入到 多组学 联合模型的阶段时,中医的“证”- ZHENG 对比于 西医 的 “症”,拥有了更丰富的内涵。人体是一个多变量的非线性系统,即使是神经、内分泌、免疫三大调节系统之间,都有着紧密关联。如何建立 “人体信息模型” -BIM ( Body Information Model),从“系统科学”的角度,借鉴中医的“易”学思想,将为下一代“整体医学”,走出一条引领之
当西医进入到 多组学 联合模型的阶段时,中医的“证”- ZHENG 对比于 西医 的 “症”,拥有了更丰富的内涵。人体是一个多变量的非线性系统,即使是神经、内分泌、免疫三大调节系统之间,都有着紧密关联。如何建立 “人体信息模型” -BIM ( Body Information Model),从“系统科学”的角度,借鉴中医的“易”学思想,将为下一代“整体医学”,走出一条引领之路! 美国 Science 2014年12月19日推出中医药特刊,刊登北京中医药大学校长徐安龙的文章:Zheng: A systems biology approach to diagnosis and treatments 为祖国医学的发展,做了很好的未来方向综述。

“证”—— 疾病诊疗的系统生物学方法
徐安龙
徐安龙
传统中医学是一种古老的医疗实践体系。它强调人体自身的统一性和人与自然环境的统一性。作为中医学的一个重要概念,“证”是人体在特定的内在或外在条件下的生理或病理概括,通常是由中医师将四诊(望、闻、问、切)所收集的资料,包括临床症状和体征,运用中医学理论进行综合分析并概括出来的疾病本质。正确辨证是疾病诊断和治疗的基础。
在西方医学中,疾病是指一种特定的病理状态,影响着人体的局部或整体,并具有特定的症状。相比之下,“证”是中医对疾病的独特定义,涵括了患者所有的症
“证”是人体在特定的内在或外在条件下的生理或病理概括,通常是由中医师将四诊(望、闻、问、切)所收集的资料,包括临床症状和体征,运用中医学理论进行综合分析并概括出来的疾病本质。正确辨证是疾病诊断和治疗的基础。
在西方医学中,疾病是指一种特定的病理状态,影响着人体的局部或整体,并具有特定的症状。相比之下,“证”是中医对疾病的独特定义,涵括了患者所有的症状。由于人体自身内部的高度统一和谐,从分子水平上完全独立地对不同疾病进行研究是十分困难的。证候的研究亦如此。再者,证候是动态变化并可相互兼夹的。有史以来,“证”一直是中医确定治法、处方遣药的重要准则。证候方面的研究缺乏,使得其潜在的生物学原理及证候、疾病和处方药物之间的联系难以被理解。既往有学者尝试将中医辨证与现代生物医学的诊断方法相结合,但其结果并未尽如人意。许多众所周知的经方,如六味地黄丸、金匮肾气丸,已经久为中医师辨证治病所用,但这类以证候为导向的治疗在证候和疗效方面仍缺乏循证医学依据。
“证”- ZHENG 对比于 西医 的 “症人体信息模型”-BIM( Body Information Model),从“系统科学”的角度,借鉴中医的“易”学思想,将为下一代“整体医学”,走出一条引领之路!
美国《证”是人体在特定的内在或外在条件下的生理或病理概括,通常是由中医师将四诊(望、闻、问、切)所收集的资料,包括临床症状和体征,运用中医学理论进行综合分析并概括出来的疾病本质。正确辨证是疾病诊断和治疗的基础。
在西方医学中,疾病是指一种特定的病理状态,影响着人体的局部或整体,并具有特定的症状。相比之下,“证”是中医对疾病的独特定义,涵括了患者所有的症
从分子水平上多尺度地对“证”的生物学基础进行研究,使其在生物学和机械论的角度上难以被理解。因此,我们提出构想,建立一种综合的证候图,以分子细胞学联系为依据,将所有的“证”联结在一起。另外,我们建议创立名为“证候组学”(Zhengome)的组学新领域,以网状结构为基础单位,从分子水平和系统水平来研究人体的层次结构。
全面地理解“证候组学”,需要引入大量的证据来源,从基因共享到蛋白质相互作用、环境因素共享、共同的治疗、临床表现,目的是为把握不同证候之间的关系。“证”通过阴阳、表里、寒热、虚实来描述患者的病理状态,从而为处方遣药提供依据。现代组学技术通过系统生物学的方法,结合生物信息学和生物网络模型,已被应用于证候间的差异性研究和寻找新的生物标记物。
例如,有研究显示,辨证为“热证”和“寒证”的类风湿性关节炎患者具有基因和代谢组学上的差异——热证患者的细胞凋亡比寒证患者更活跃。再者,有学者通过采用一种以网状结构为基础的计算模型,从神经-内分泌-免疫的角度理解证候的涵义,结果发现寒证和热证与代谢-免疫失衡密切相关。有人对黄疸患者的尿液代谢组学及“阳黄”(急性)与“阴黄”(慢性)两种分型进行研究,并找出几种生物标志物代谢产物。
然而,目前大多数研究仅仅依靠一种或两种指纹图谱技术的方法,而缺乏一种能将来自不同组学的数据整合在一起的方法。这些研究没有将分子水平数据的分析与临床变量结合在一起,由此可能失去了产生更具说服力的结论的机遇。鉴于既往研究的局限性,未来我们需致力于对大量不同证型患者的数据进行各类组学水平的综合分析,并需涵盖疾病预后和治疗工具方面的研究。再者,将患者的临床信息和分子水平数据结合在一起,可以为证候的理论解释提供循证依据。证候可以随着疾病的进展而动态变化。在疾病的各个不同阶段进行正确辨证,能为及时调整方药提供有利依据。采用动态的网状结构模型,疾病病程可以被定位为网状结构中的时空变化。
 动态调整处方治疗后所发生的证候变化可用于辨别动态生物网状结构中的重要因素。正确的网络微扰模型和稳健性及拓扑分析可以揭示疾病进展或演变潜在的相关基因和治疗靶点。在建立模型和模型的过程中,需将疾病在特定证候中不同方面的表现(例如主症和并发症)、心理因素、社会因素和环境因素之间的关系考虑在内,旨在揭示复杂疾病的动态属性。“证候组学”与动态模型的结合,对建立精准量化的证候研究模型、创立新的疾病研究系统有着潜在意义。
尽管基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学和代谢组学已取得较大进展,合理的药物设计和新药研发仍经常遭遇失败,耗费巨大,阻碍着现代药物的研发。
纵观中医药发展史,在传统药物的研发中,以证候为导向的药物研发取得了巨大的成就。但是这对于西方医学来说是一种全新的模式。因此,如何将以证候为导向的药物研发融入到现代药物研发的潮流中,将是一大难题。
在此,我们提出在系统药理学框架中建立“从证到中医”和“从中医到证”的策略,旨在研究生物系统和开发新型的治疗方法。
“从证到中医”从证候的诊断到中药处方之间提供了渠道,包括证候的辨别、证候和相关的基因、蛋白及药效反向定位的识别、网状结构系统的构建与分析和最终找出有效的中药疗法。实际上,这样的策略可作为一种反向定位和筛选的途径,从适用于多种证型及相关疾病的天然药物中寻找并研发新药,目的是为了帮助研究者找出药用植物、多成分中药处方或复方合剂的活性成分。
而这种新策略已经成功应用于我们的一个研究中。我们在补益气血的中药中找到其有效成分、靶点及在治疗气血不足证中的作用途径。“从中医到证”是指从中药或中药复方到证候辨别的整个系统评估的过程,包括中药的采集与分类,药物吸收、分布、代谢、排泄和具有毒性的成分,药物靶向的检查和组织定位,构建和分析网状结构系统,最终辨别证候/疾病。这种策略可能有助于在天然药物中找出新型的多靶点药物。
举个非常显著的例子,就是冠心病气虚血瘀证和相应辨证用药的系统分析,结果提示该类用药中的活血药具有扩张血管、改善循环、降低血液粘度、调节血脂的作用,而补气药具有促进能量代谢和抗炎的疗效。
“从中医到证”的策略有助于阐释中药及其复方的药理学作用。在我们正在开展的“脾虚证”研究中,我们采用sapas、rna测序、脂类代谢组学、蛋白质代谢组学和转录组学的方法对患者提供的标本进行分析,以解释脾虚证的发病机制和人体复杂反应。
动态调整处方治疗后所发生的证候变化可用于辨别动态生物网状结构中的重要因素。正确的网络微扰模型和稳健性及拓扑分析可以揭示疾病进展或演变潜在的相关基因和治疗靶点。在建立模型和模型的过程中,需将疾病在特定证候中不同方面的表现(例如主症和并发症)、心理因素、社会因素和环境因素之间的关系考虑在内,旨在揭示复杂疾病的动态属性。“证候组学”与动态模型的结合,对建立精准量化的证候研究模型、创立新的疾病研究系统有着潜在意义。
尽管基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学和代谢组学已取得较大进展,合理的药物设计和新药研发仍经常遭遇失败,耗费巨大,阻碍着现代药物的研发。
纵观中医药发展史,在传统药物的研发中,以证候为导向的药物研发取得了巨大的成就。但是这对于西方医学来说是一种全新的模式。因此,如何将以证候为导向的药物研发融入到现代药物研发的潮流中,将是一大难题。
在此,我们提出在系统药理学框架中建立“从证到中医”和“从中医到证”的策略,旨在研究生物系统和开发新型的治疗方法。
“从证到中医”从证候的诊断到中药处方之间提供了渠道,包括证候的辨别、证候和相关的基因、蛋白及药效反向定位的识别、网状结构系统的构建与分析和最终找出有效的中药疗法。实际上,这样的策略可作为一种反向定位和筛选的途径,从适用于多种证型及相关疾病的天然药物中寻找并研发新药,目的是为了帮助研究者找出药用植物、多成分中药处方或复方合剂的活性成分。
而这种新策略已经成功应用于我们的一个研究中。我们在补益气血的中药中找到其有效成分、靶点及在治疗气血不足证中的作用途径。“从中医到证”是指从中药或中药复方到证候辨别的整个系统评估的过程,包括中药的采集与分类,药物吸收、分布、代谢、排泄和具有毒性的成分,药物靶向的检查和组织定位,构建和分析网状结构系统,最终辨别证候/疾病。这种策略可能有助于在天然药物中找出新型的多靶点药物。
举个非常显著的例子,就是冠心病气虚血瘀证和相应辨证用药的系统分析,结果提示该类用药中的活血药具有扩张血管、改善循环、降低血液粘度、调节血脂的作用,而补气药具有促进能量代谢和抗炎的疗效。
“从中医到证”的策略有助于阐释中药及其复方的药理学作用。在我们正在开展的“脾虚证”研究中,我们采用sapas、rna测序、脂类代谢组学、蛋白质代谢组学和转录组学的方法对患者提供的标本进行分析,以解释脾虚证的发病机制和人体复杂反应。
 我们准备根据“从中医到证”的策略,从药物研发的角度,系统地研究广泛用于治疗脾虚证的四君子汤,目的在于探讨此方为何能够调节免疫反应、促进血液循环和改善胃肠道功能。
尽管以证候为导向的药物研发已经取得一定进展,但其未来的发展仍需要多学科技术的结合和创新。这将促进对疾病的多因素理解和新型疗法的发展。
我们准备根据“从中医到证”的策略,从药物研发的角度,系统地研究广泛用于治疗脾虚证的四君子汤,目的在于探讨此方为何能够调节免疫反应、促进血液循环和改善胃肠道功能。
尽管以证候为导向的药物研发已经取得一定进展,但其未来的发展仍需要多学科技术的结合和创新。这将促进对疾病的多因素理解和新型疗法的发展。
(译者后记:粗略翻译的一篇文章,供大家参考学习。学识尚浅,对
于文中的不足之处,敬请各位老师、同学、专业人士批评指正!谢谢!)
原始出处:
Zheng: A systems biologyapproach to diagnosis and treatments
TraditionalChinese medicine (TCM) is an ancient medical practice system which emphasizesregulating the integrity of the human body and its interrelationship withnatural environments. As a key concept in TCM, Zheng (meaning syndrome orpattern)is the overall physiological and/or pathological pattern of the humanbody in response to a given internal and external condition, which usually isan abstraction of internal disharmony defined by a comprehensive analysis ofthe clinical symptoms and signs gathered by a practitioner using inspection,auscultation, olfaction, interrogation, and palpation of the pulses (1).Correctly identifying the Zheng is fundamental for the diagnosis and treatmentof diseases.to systems level is important for advancing the identificationandtreatment of these syndromes, and for providing more objective and quantitativediagnostic criteria.
In Western medicine, a disease is a particular abnormal and pathological conditionthat affects part or all of the human body and is often construed as a medicalcondition associated with specific symptoms. By contrast, Zheng puts forth avery different definition of a disease and encompasses all of the symptoms apatient presents.
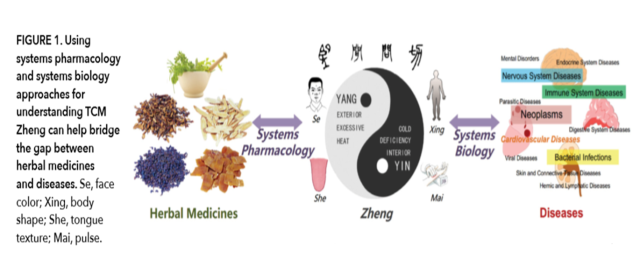
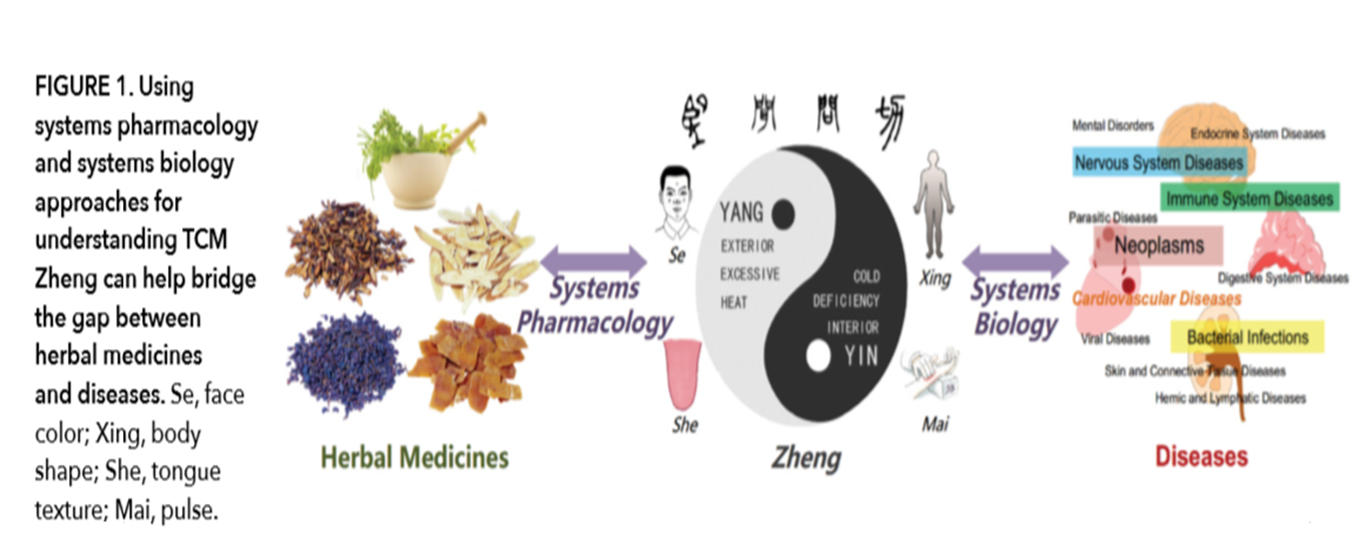
Becauseof the highly interconnected nature of the human interactome, it is difficultto study different diseases at the molecular level completely independent ofone another (3), and this issue also applies to Zhengs. Moreover, Zhengs aredynamic with changing boundaries, overlapping symptoms,Moreover, Zheng has beenhistorically applied as the key pathological principle guiding the prescriptionof herbal formulas (Figure 1).
A lackof research on Zheng has left us with little understanding of its underlyingbiology or the relationships between different Zhengs, diseases, and drugs.Moreover, there have been attempts to integrate Zheng differentiation withmodern biomedical diagnostic methods, though these efforts have not achievedthe desired results (2). Many well-known herbal recipes, such as Liu Wei DiHuang Wan and Jin Kui Shen Qi Wan, have long been used for the clinicaltreatment of Zheng disorders; however, Zheng-guided treatments are still scarcedue to the lack of evidence-based interpretations of syndromes and treatmentefficacies. Thus, investigating the biological basis of Zhengs from a molecularand a multiscale nature, which makes them difficult to understand at abiological and mechanistic level. Thus, we propose that a comprehensive Zhengmap be constructed that links together all the Zhengs based on their molecularand cellular relationships. Further, we suggest creating the “Zhengome” as a new 'omics field, in which a networkis the basic research unit used to investigate the hierarchy present in thehuman body,from the molecular to the systems level. Acomprehensiveunderstanding of the Zhengome requires us to bring togethermultiple sources of evidence, from shared genes to proteinprotein interactions,shared environmental factors, common treatments, and phenotypic and clinicalmanifestations, in order to capture the relationships between the differentZhengs.
Zheng uses the Yin-Yang, exterior-interior, cold-heat, and deficiency-excessdefinitions to describe patients’ conditions, which are then managed byZheng-specific recipes (Figure 1). Modern 'omics techniques combined withbioinformatics and bionetwork models through a systems biology approach havebeen applied to investigate the differences between Zhengs and to identifynovel biomarkers. For instance, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients differentiatedon the basis of “hot” and “cold” Zhengs have been shown to be associatedwith different underlying genomic and metabolomic profiles, with the RA hotgroup showing more apoptotic activity than the cold group (4). Additionally, Liet al. used a network-based computational model to understand Zheng in thecontext of the neuro-endocrine-immune network and found that cold and hotZhengs were closely related to a metabolism-immune imbalance (5). Wang andcolleagues investigated the urine metabolome of patients with jaundice syndromeand its two subtypes of Yang Huang (acute) and Yin Huang (chronic), andidentified several biomarker metabolites (6). However, most of the currentstudies have relied on only one or two approaches for molecular profiling and havelacked an efficient method to integrate data obtained at different 'omiclevels. These studies also did not look at combining the analysis of moleculardata with clinical variables, possibly missing an opportunity to generate moreconvincing conclusions. Considering the limitations of past studies, futureefforts should integrate an analysis for all levels of 'omics (e.g., genomics,transcriptomics, epigenomics, and proteomics) data from a large number ofpatient samples for different Zhengs and include an investigation of theprognostic and therapeutic utilities of the data as a whole. Moreover,combining these molecular data with patients’ clinical information could provideevidence-based theoretical interpretations for Zhengs and enable an assessmentof Zheng-based therapeutic approaches.
Zhengs may change dynamically during disease progression. Differentiating the specificZheng involved in each stage of a disease could provide valuable guidance forprescribing a dynamic therapeutic recipe. Using dynamic network modeling, adisease process can be conceptualized as spatio-temporal changes in networkstructures. The changes associated with a Zheng under dynamic therapy can beused to identify the key factors in the dynamic biological networks. Appropriatenetwork perturbation models and subsequent robustness and topology analysiscould help unveil potential disease-related genes or therapeutic targetsinvolved in a disease’s progression or evolution (7). Therelationships between the different aspects of a disease (e.g., main symptomsversus complications) in a specific Zheng as well as the psychological, social,and even environmental factors should be taken into account during the modelingand simulation process in order to uncover the dynamic nature of complexdiseases.Combining a Zhengome approach with dynamic modeling has the potentialfor establishing an accurate and quantitative Zheng research model, as well asfor creating a new system for performing disease research.
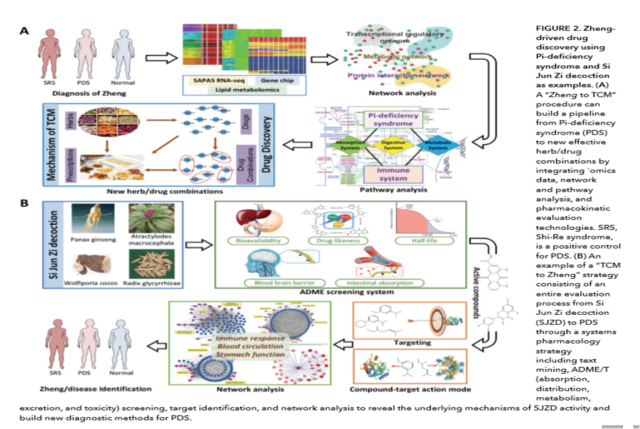
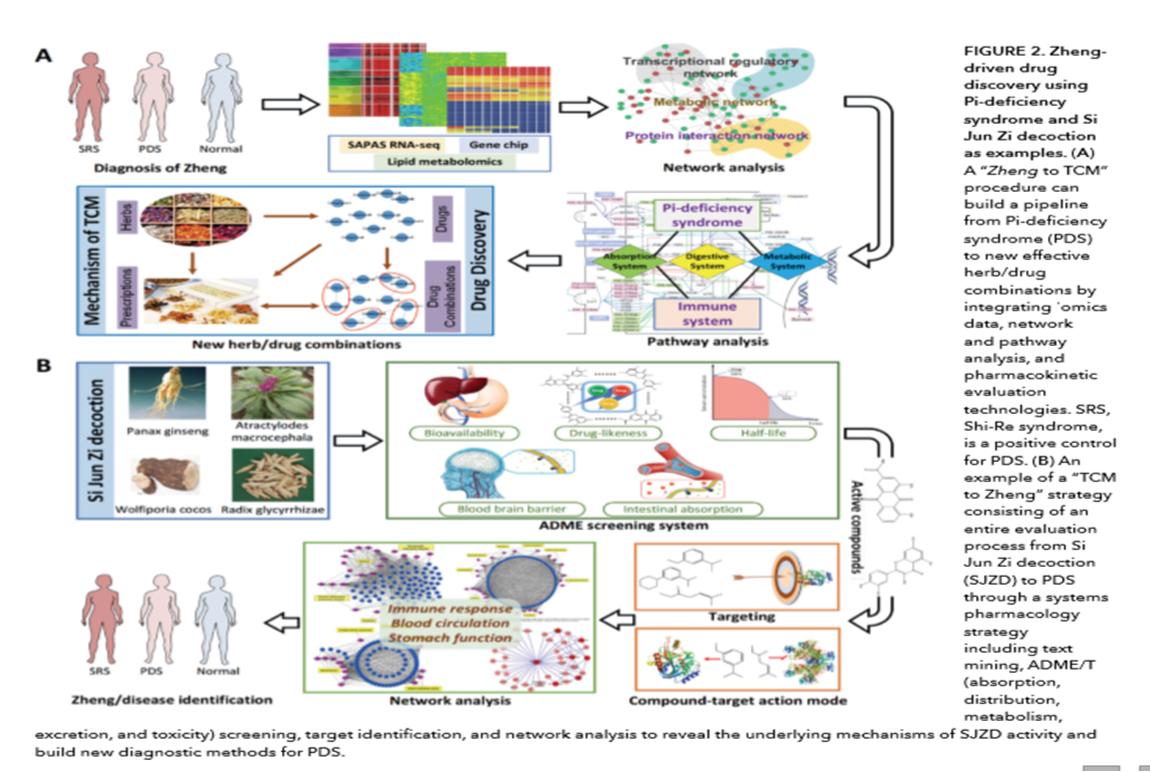
Despite considerable progress in genome, transcriptome,proteome, and metabolome-basedhigh throughput screening methods and in rational drug design, drug discoveryoften encounters considerable costly failures that challenge the fidelity ofthe modern drug discovery system. Zheng-driven drug discovery has showntremendous success for traditional drug discovery throughout Chinese medicine’s history. However, since this concept iscompletely new to Western medicine, it is no easy task to incorporateZheng-driven drug discovery into modern drug discovery workflows. Here, wepropose the “Zheng to TCM” and “TCM to Zheng” strategies within the framework of systemspharmacology to investigate biological systems and develop new therapeutics(Figure 2). The first strategy, Zheng to TCM, proposes developing a pipelinefrom Zheng diagnoses to TCM drugs,including differentiating Zhengs, identifyingZheng-related diseases and the associated genes and proteins, reverse targetingof drug effects, constructing and analyzing network/systems, and finally identifyingeffective herbal medicines (8). In effect, this strategy can be considered areverse targeting and screening approach that is designed to uncover drugs fromnatural products that can target multiple Zhengs or related diseases. The goalof this method is to help researchers identify the active components withinmedicinal plants and multi-ingredient synergistic herbal formulas or drugcombinations (9). In fact, this novel strategy has already been successfullyapplied in a qi-blood study, where we identified the active compounds in theqi-enriching and blood-tonifying herbs, their targets, and the correspondingpathways involved in the treatment of qi and blood deficiency syndromes (8).The second strategy, TCM to Zheng, consists of a wholesystem evaluation processstarting with herbs or herbal formulas and culminating in identifying theZhengs. This process includes the initial collection and classification ofherbal medicines; screening the ingredients for absorption, distribution,metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADME/T); performing targeted drugscreenings and tissue localization; constructing and analyzing networks; andfinally identifying Zhengs/diseases (10). Using this strategy, it is possibleto identify novel multitarget drugs in natural products (11). One particularlystriking example is the systematic analysis of blood stasis and qi deficiencysyndrome in coronary heart disease and the herbal drugs used to treat thesyndromes.The results indicate that the herbs for eliminating blood stasis havepharmacological activity that acts to dilate blood vessel, improve themicrocirculation, reduce blood viscosity, and regulate blood lipid, whileqi-enhancing herbs have the potential for enhancing energy metabolism andantiinflammatory activity (12). The TCM to Zheng strategy can also help toelucidate the pharmacological effectiveness of herbs and formulas.
In ourongoing work investigating Pi-deficiency syndrome(PDS) in the context of Zheng,we are analyzing patient samples using the sequencing alternativepolyadenylation sites (SAPAS) method, RNA sequencing (13), lipid metabolomics,proteomics, and transcriptomics in order to decipher the pathogenesis andcomplex responses of the human body to PDS. From a drug developmentperspective, we plan to systematically investigate the Si Jun Zi decoction, awidely used herbal recipe for PDS, within the framework of the “TCM to Zheng” strategy, so as to understand why thisrecipe can regulate the immune response, stimulate blood circulation, andadjust gastrointestinal digestive functions. Despite the progress inZheng-guided drug discovery, its future success requires the integration ofmultidisciplinary technologies, together with further innovations in thesetechnologies, to facilitate the understanding of multifactorial diseases andthe development of new therapies.
References
1. F.Cheung, Nature 480, S82 (2011).
2. A.Lu, M. Jiang, C. Zhang, K. Chan, J. Ethnopharmacol. 141, 549
(2012).
3. A.L. Barabasi, N. Gulbahce, J. Loscalzo, Nat. Rev. Genet. 12, 56
(2011).
4. H.van Wietmarschen et al., J. Clin. Rheumatol. 15, 330 (2009).
5. S.Li et al., IET Syst. Biol. 1, 51 (2007).
6. X.Wang et al., Mol. Cell. Proteomics 11, 370 (2012).
7. P.Csermely, T. Korcsmaros, H. J. M. Kiss, G. London, R. Nussinov,
Pharmacol.Therapeut. 138, 333 (2013).
8. J.Liu et al., Evid. Based Compl. Alt. Med. 2013, 938764 (2013).
9. P.Li et al., J. Ethnopharmacol. 151, 93 (2014).
10. C.Huang et al., Brief. Bioinform. 15, 710 (2014).
11. C.Zheng et al., Mol. Diversity 18, 621 (2014).
12. W.Zhou, Y. Wang, J. Ethnopharmacol. 151, 66 (2014).
13. Y.G. Fu et al., Genome Res. 21, 741 (2011).
小提示:本篇资讯需要登录阅读,点击跳转登录
版权声明:
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言








#系统生物#
59
很不错的文章
151
#SCIE#
62
#生物学#
72
第一作者是谁?
139