Brain:脑损伤数据绘制大脑智力图谱
2012-04-14 T.Shen 生物谷
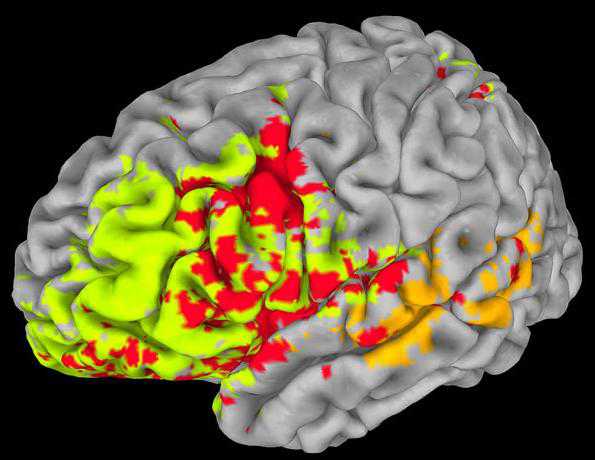
A new study found that specific structures, primarily on the left side of the brain, are vital to general intelligence and executive function(Credit: Photo courtesy Aron Barbey) 一项研究发现大脑的特殊结构域,尤其是大脑的

A new study found that specific structures, primarily on the left side of the brain, are vital to general intelligence and executive function(Credit: Photo courtesy Aron Barbey)
一项研究发现大脑的特殊结构域,尤其是大脑的左边区域对于智力以及执行能力尤为重要
Copyright ©版权归生物谷所有,若未得到Bioon授权,请勿转载。
近日,科学家报道他们已经绘制出了大脑智力分布的物理结构图,这是目前为止最大规模的对大脑结构的综合分析,对于普通理解力以及智力功能的理解,比如言语理解力以及工作记忆等尤为重要。这项研究刊登在了国际杂志Brain上,研究者招募的志愿者为182名有严重脑部损伤的越南退伍军人。伊利诺伊大学的研究者Aron Barbey表示,对于发现病人脑部损伤或者发现大脑病灶非常困难,中风引起的大脑损伤经常会损伤大脑的很多区域,对于识别大脑特殊结构的认知区域非常复杂,需要花费大量时间来进行研究。
Barbey说,本研究中分析大脑损伤的病灶让我们可以推测特殊的脑结构对于机体行为的重要性。通过学习特殊大脑区域的损伤如何能够产生特殊的认知障碍,我们可以绘制大脑的体系结构,识别大脑结构对于维持特殊智力能力的作用。研究者通过对参与者进行大脑CT扫描,以及后续的认知测试。最终研究者们得到了参与者的大脑皮质图谱,随后将其分为3000个的三维单位(voxel,体元),研究者对这种voxel损伤的病人进行分析并且对比他们的认知能力,最终可以确定对特殊认知功能有必要的大脑区域以及大脑的哪些结构行使智力功能发挥的区域。研究者表示,普通智力依靠一个显著地局限的神经系统,而且数个大脑区域以及其之间的联系对于普通智力的发挥至关重要。
研究者发现的这些关键结构位于大脑左前额叶、左颞皮质以及左顶叶皮质处,而且大脑的闹白质将他们联系起来。研究者同时也发现了大脑中行使计划、自控以及其它执行力相关的大脑区域。这项研究揭示了机体的智力并不是一带与大脑的一块区域或者整个大脑,而是依赖于大脑特定区域之间共同的协作。
文章中,研究者的发现将对于将来进行智力的生物学研究提供了新的研究线索,探寻大脑、基因、营养以及环境之间的相互作用关系对于我们了解塑造大脑的发展以及智力的发展进化非常重要。(生物谷:T.Shen编译)
Copyright ©版权归生物谷所有,若未得到Bioon授权,请勿转载。

doi:10.1093/brain/aws021
PMC:
PMID:
An integrative architecture for general intelligence and executive function revealed by lesion mapping
Aron K. Barbey1,2,3,4,5, Roberto Colom6, Jeffrey Solomon7, Frank Krueger8, Chad Forbes9 and Jordan Grafman10
Although cognitive neuroscience has made remarkable progress in understanding the involvement of the prefrontal cortex in executive control, the broader functional networks that support high-level cognition and give rise to general intelligence remain to be well characterized. Here, we investigated the neural substrates of the general factor of intelligence (g) and executive function in 182 patients with focal brain damage using voxel-based lesion–symptom mapping. The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale and Delis–Kaplan Executive Function System were used to derive measures of g and executive function, respectively. Impaired performance on these measures was associated with damage to a distributed network of left lateralized brain areas, including regions of frontal and parietal cortex and white matter association tracts, which bind these areas into a coordinated system. The observed findings support an integrative framework for understanding the architecture of general intelligence and executive function, supporting their reliance upon a shared fronto-parietal network for the integration and control of cognitive representations and making specific recommendations for the application of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale and Delis–Kaplan Executive Function System to the study of high-level cognition in health and disease.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言











#损伤#
62